May-Panama
April-Kenya



March-Ireland
February- Morocco




December-Peru

November-Mongolia
October-Mali
September-Great Britain
June-Sudan

May-Mexico


April-Iceland





March- Guatemala
February- Nicaragua
January- Italy



December- Israel







November- Bangladesh


October- France


From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This article is about the country. For other uses, see France (disambiguation).
| French Republic
République française (French)
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
| Motto: "Liberté, égalité, fraternité" (French) "Liberty, Equality, Fraternity" | ||||||
| Anthem: "La Marseillaise" | ||||||
|
Territory of the French Republic[I]
| ||||||
|
| ||||||
| Capital and largest city | Paris 48°51.4′N 2°21.05′E | |||||
| Official language and national language | French[II] | |||||
| Demonym | French | |||||
| Government | Unitarysemi‑presidential constitutional republic | |||||
| • | President | François Hollande | ||||
| • | Prime Minister | Manuel Valls | ||||
| • | President of the Senate | Gérard Larcher | ||||
| • | President of the National Assembly | Claude Bartolone | ||||
| Legislature | Parliament | |||||
| • | Upper house | Senate | ||||
| • | Lower house | National Assembly | ||||
| Establishment | ||||||
| • | Francia unified | 486 | ||||
| • | Treaty of Verdun | August 843 | ||||
| • | Republic established | 22 September 1792 | ||||
| • | Founded the EEC | 1 January 1958 | ||||
| • | Current constitution | 4 October 1958 | ||||
| Area | ||||||
| • | Total | 643,801 km2[VI][1](41st) 248,600 sq mi | ||||
| • | Metropolitan France(IGN) | 551,695 km2[VII](50th) 213,010 sq mi | ||||
| • | Metropolitan France(Cadastre) | 543,940.9 km2[VIII][2](50th) 210,026 sq mi | ||||
| Population | ||||||
| • | Total 2016 estimate | 66,736,000[VI][3](20th) | ||||
| • | Metropolitan France June 2016 estimate | 64,590,000[4] (22nd) | ||||
| • | Density | 116/km2[IX] (89th) 301/sq mi | ||||
| GDP (PPP) | 2015 estimate | |||||
| • | Total | $2.647 trillion (10th) | ||||
| • | Per capita | $41,181[5] (24th) | ||||
| GDP (nominal) | 2015 estimate | |||||
| • | Total | $2.422 trillion (6th) | ||||
| • | Per capita | $37,675[5] (20th) | ||||
| Gini (2013) | 30.1[6] medium | |||||
| HDI (2014) | very high · 22nd | |||||
| Currency | ||||||
| Time zone | CET[XII] (UTC+1) | |||||
| • | Summer (DST) | CEST[XIII] (UTC+2) | ||||
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy | |||||
| Drives on the | right | |||||
| Calling code | +33[XIV] | |||||
| ISO 3166 code | FR | |||||
| Internet TLD | .fr[XV] | |||||
France (French: [fʁɑ̃s]), officially the French Republic (French: République française [ʁepyblik fʁɑ̃sɛz]), is atranscontinental sovereign state comprising territory in western Europe and several overseas regions and territories.[XVI] The European, or metropolitan, area of France extends from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea, and from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean. Overseas France include French Guiana on theSouth American continent and several island territories in the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian oceans. France spans 643,801 square kilometres (248,573 sq mi)[1] and has a total population of 66.7 million.[VI][8] It is a unitary semi-presidential republic with the capital in Paris, the country's largest city and main cultural and commercial centre. During the Iron Age, what is now metropolitan France was inhabited by the Gauls, a Celtic people. The area was annexed in 51 BC by Rome, which held Gaul until 486, when the Germanic Franks conquered the region and formed the Kingdom of France.
France emerged as a major European power in the Late Middle Ages, with its victory in the Hundred Years' War (1337 to 1453) strengthening state-building and political centralisation. During the Renaissance, French culture flourished and a global colonial empire was established, which by the 20th century would be the second largest in the world.[9]The 16th century was dominated by religious civil wars between Catholics and Protestants (Huguenots). France became Europe's dominant cultural, political, and military power under Louis XIV.[10] In the late 18th century, the French Revolution overthrew the absolute monarchy, established one of modern history's earliest republics, and saw the drafting of the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen, which expresses the nation's ideals to this day.
In the 19th century Napoleon took power and established the First French Empire, whose subsequent Napoleonic Wars shaped the course of continental Europe. Following the collapse of the Empire, France endured a tumultuous succession of governments culminating with the establishment of the French Third Republic in 1870. France was a major participant in the First World War, from which it emerged victorious, and was one of the Allied Powers in the Second World War, but came under occupation by the Axis Powers in 1940. Following liberation in 1944, a Fourth Republic was established and later dissolved in the course of the Algerian War. The Fifth Republic, led by Charles de Gaulle, was formed in 1958 and remains to this day. Algeria and the colonies in Indochina became independent in the 1950s after long, bloody wars. Nearly all the other colonies became independent in the 1960s with minimal controversy and typically retained close economic and military connections with France. Since the second half of the 20th century, France is a driving force of European integration, along with its ally Germany.
France has long been a global centre of art, science, and philosophy. It hosts Europe's fourth-largest number of cultural UNESCO World Heritage Sites and receives around 83 million foreign tourists annually, the most of any country in the world.[11] France is a developed country with the world's sixth-largest economy by nominal GDP[12] and ninth-largest by purchasing power parity.[13] In terms of aggregate household wealth, it ranks fourth in the world.[14] France performs well in international rankings of education, health care, life expectancy, and human development.[15][16]France remains a great power in the world,[17] being a founding member of the United Nations, where it serves as one of the five permanent members of the UN Security Council, and a founding and leading member state of the European Union (EU).[18] It is also a member of the Group of 7, North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), the World Trade Organization (WTO), and La Francophonie.
September- USA
May- Mexico
April-Japan


March-Thailand

February- Cuba
January-Norway
December- South Africa
November-Canada
Dialing code: +1
Population: 35.16 million (2013) World Bank
Currency: Canadian dollar
Provinces: Ontario, British Columbia, Québec, Alberta, More
| Continent | North America |
|---|---|
| Region | Northern America |
| Coordinates | 60°00′N 95°00′W |
| Area | Ranked 2nd |
| • Total | 9,984,671 km2 (3,855,103 sq mi) |
| • Land | 91.08% |
| • Water | 8.92% |
| Coastline | 202,080 km (125,570 mi) |
| Borders | 8,893 km |
| Highest point | Mount Logan, 5,959 m (19,551 ft) |
| Lowest point | Atlantic Ocean, Sea Level |
| Longest river | Mackenzie River, 4,241 km (2,635 mi) |
| Largest lake | Great Bear Lake 31,153 km2 (12,028 sq mi) |
| Climate | temperate in south to subarctic or arctic in north |
| Terrain | mostly plains with mountains in west and lowlands in southeast |
| Natural Resources | iron ore, nickel, zinc, copper, gold,lead, molybdenum, potash, diamonds, silver, fish, timber, wildlife, coal,petroleum, natural gas, hydropower |
| Natural Hazards | permafrost, cyclonic storms,tornadoes, forest fires |
| Environmental Issues | air and water pollution, acid rains |
October - France

 Louvre Museum Eiffel Tower
Louvre Museum Eiffel TowerLocated In Europe
France
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This article is about the country. For other uses, see France (disambiguation).
| French Republic
République française (French)
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
| Motto: "Liberté, égalité, fraternité" (French) "Liberty, Equality, Fraternity" | ||||||
| Anthem: "La Marseillaise" | ||||||
|
Territory of the French Republic[I]
| ||||||
|
| ||||||
| Capital and largest city | Paris 48°51.4′N 2°21.05′E | |||||
| Official language and national language | French[II] | |||||
| Demonym | French | |||||
| Government | Unitarysemi‑presidential constitutional republic | |||||
| • | President | François Hollande | ||||
| • | Prime Minister | Manuel Valls | ||||
| • | President of the Senate | Gérard Larcher | ||||
| • | President of the National Assembly | Claude Bartolone | ||||
| Legislature | Parliament | |||||
| • | Upper house | Senate | ||||
| • | Lower house | National Assembly | ||||
| Establishment | ||||||
| • | Francia unified | 486 | ||||
| • | Treaty of Verdun | August 843 | ||||
| • | Republic established | 22 September 1792 | ||||
| • | Founded the EEC | 1 January 1958 | ||||
| • | Current constitution | 4 October 1958 | ||||
| Area | ||||||
| • | Total | 643,801 km2[VI][1](41st) 248,600 sq mi | ||||
| • | Metropolitan France(IGN) | 551,695 km2[VII](50th) 213,010 sq mi | ||||
| • | Metropolitan France(Cadastre) | 543,940.9 km2[VIII][2](50th) 210,026 sq mi | ||||
| Population | ||||||
| • | Total 2016 estimate | 66,736,000[VI][3](20th) | ||||
| • | Metropolitan France June 2016 estimate | 64,590,000[4] (22nd) | ||||
| • | Density | 116/km2[IX] (89th) 301/sq mi | ||||
| GDP (PPP) | 2015 estimate | |||||
| • | Total | $2.647 trillion (10th) | ||||
| • | Per capita | $41,181[5] (24th) | ||||
| GDP (nominal) | 2015 estimate | |||||
| • | Total | $2.422 trillion (6th) | ||||
| • | Per capita | $37,675[5] (20th) | ||||
| Gini (2013) | 30.1[6] medium | |||||
| HDI (2014) | very high · 22nd | |||||
| Currency | ||||||
| Time zone | CET[XII] (UTC+1) | |||||
| • | Summer (DST) | CEST[XIII] (UTC+2) | ||||
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy | |||||
| Drives on the | right | |||||
| Calling code | +33[XIV] | |||||
| ISO 3166 code | FR | |||||
| Internet TLD | .fr[XV] | |||||
France (French: [fʁɑ̃s]), officially the French Republic (French: République française [ʁepyblik fʁɑ̃sɛz]), is atranscontinental sovereign state comprising territory in western Europe and several overseas regions and territories.[XVI] The European, or metropolitan, area of France extends from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea, and from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean. Overseas France include French Guiana on theSouth American continent and several island territories in the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian oceans. France spans 643,801 square kilometres (248,573 sq mi)[1] and has a total population of 66.7 million.[VI][8] It is a unitary semi-presidential republic with the capital in Paris, the country's largest city and main cultural and commercial centre. During the Iron Age, what is now metropolitan France was inhabited by the Gauls, a Celtic people. The area was annexed in 51 BC by Rome, which held Gaul until 486, when the Germanic Franks conquered the region and formed the Kingdom of France.
France emerged as a major European power in the Late Middle Ages, with its victory in the Hundred Years' War (1337 to 1453) strengthening state-building and political centralisation. During the Renaissance, French culture flourished and a global colonial empire was established, which by the 20th century would be the second largest in the world.[9]The 16th century was dominated by religious civil wars between Catholics and Protestants (Huguenots). France became Europe's dominant cultural, political, and military power under Louis XIV.[10] In the late 18th century, the French Revolution overthrew the absolute monarchy, established one of modern history's earliest republics, and saw the drafting of the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen, which expresses the nation's ideals to this day.
In the 19th century Napoleon took power and established the First French Empire, whose subsequent Napoleonic Wars shaped the course of continental Europe. Following the collapse of the Empire, France endured a tumultuous succession of governments culminating with the establishment of the French Third Republic in 1870. France was a major participant in the First World War, from which it emerged victorious, and was one of the Allied Powers in the Second World War, but came under occupation by the Axis Powers in 1940. Following liberation in 1944, a Fourth Republic was established and later dissolved in the course of the Algerian War. The Fifth Republic, led by Charles de Gaulle, was formed in 1958 and remains to this day. Algeria and the colonies in Indochina became independent in the 1950s after long, bloody wars. Nearly all the other colonies became independent in the 1960s with minimal controversy and typically retained close economic and military connections with France. Since the second half of the 20th century, France is a driving force of European integration, along with its ally Germany.
France has long been a global centre of art, science, and philosophy. It hosts Europe's fourth-largest number of cultural UNESCO World Heritage Sites and receives around 83 million foreign tourists annually, the most of any country in the world.[11] France is a developed country with the world's sixth-largest economy by nominal GDP[12] and ninth-largest by purchasing power parity.[13] In terms of aggregate household wealth, it ranks fourth in the world.[14] France performs well in international rankings of education, health care, life expectancy, and human development.[15][16]France remains a great power in the world,[17] being a founding member of the United Nations, where it serves as one of the five permanent members of the UN Security Council, and a founding and leading member state of the European Union (EU).[18] It is also a member of the Group of 7, North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), the World Trade Organization (WTO), and La Francophonie.
September - Brazil
Located in South America
Brazil occupies a large area along the eastern coast of South America and includes much of the continent's interior, sharing land borders with Uruguay to the south; Argentina and Paraguay to the southwest; Bolivia and Peru to the west;Colombia to the northwest; and Venezuela, Guyana, Suriname and France (French overseas region of French Guiana) to the north. It shares a border with every South American country except Ecuador and Chile.
Brazil is the fifth largest country in the world, and third largest in the Americas, with a total area of 8,515,767.049 km2(3,287,956 sq mi), including 55,455 km2 (21,411 sq mi) of water. It spans four time zones. Brazil is the only country in the world that has the equator and the Tropic of Capricorn running through it. It is also the only country to have contiguous territory both inside and outside the tropics. Brazilian topography is also diverse and includes hills, mountains, plains, highlands, and scrublands. Much of the terrain lies between 200 metres (660 ft) and 800 metres (2,600 ft) in elevation. The main upland area occupies most of the southern half of the country. The northwestern parts of the plateau consist of broad, rolling terrain broken by low, rounded hills. Brazil has a dense and complex system of rivers, one of the world's most extensive, with eight major drainage basins, all of which drain into the Atlantic.[146] Major rivers include the Amazon (the world's second-longest river and the largest in terms of volume of water), the Paraná and its major tributary the Iguaçu (which includes the Iguazu Falls), the Negro, São Francisco, Xingu, Madeira and Tapajós rivers.
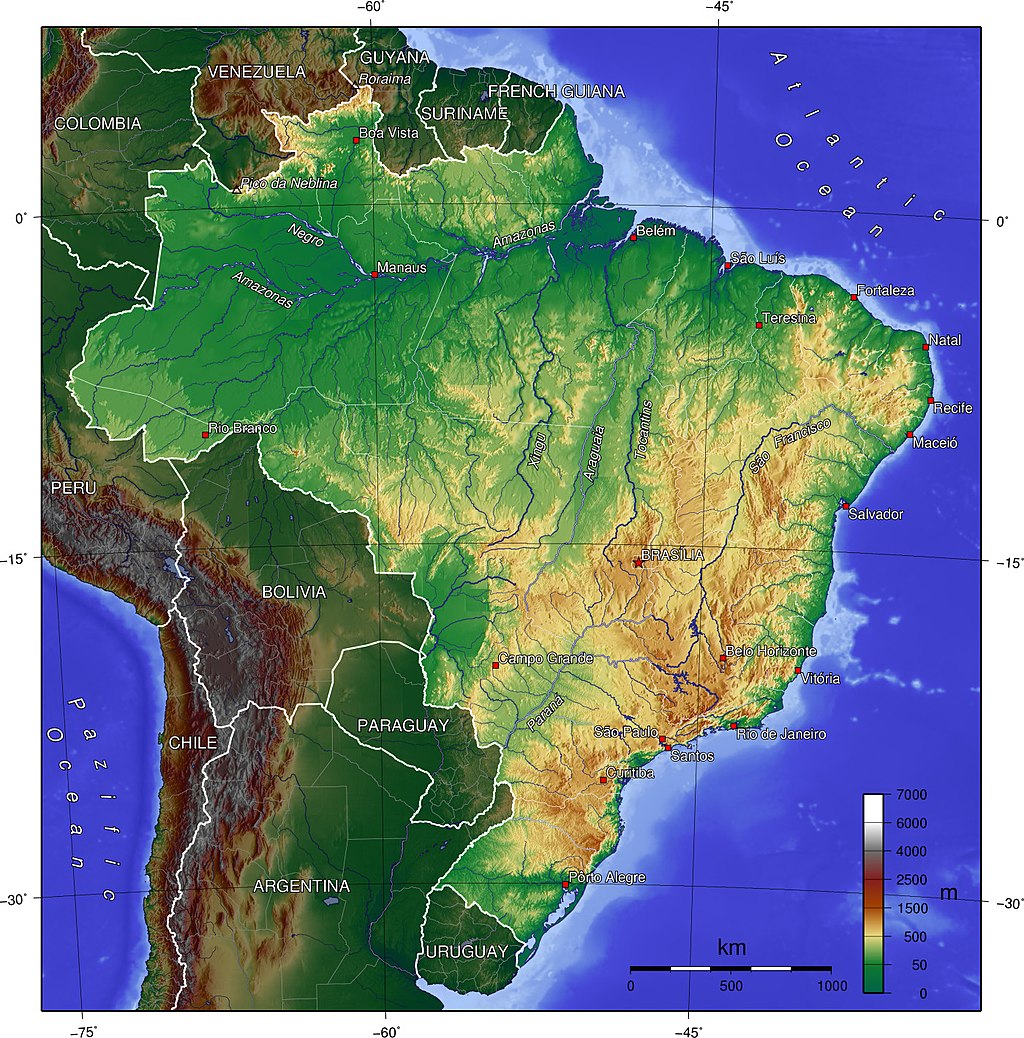
Brazil occupies a large area along the eastern coast of South America and includes much of the continent's interior, sharing land borders with Uruguay to the south; Argentina and Paraguay to the southwest; Bolivia and Peru to the west;Colombia to the northwest; and Venezuela, Guyana, Suriname and France (French overseas region of French Guiana) to the north. It shares a border with every South American country except Ecuador and Chile.
Brazil is the fifth largest country in the world, and third largest in the Americas, with a total area of 8,515,767.049 km2(3,287,956 sq mi), including 55,455 km2 (21,411 sq mi) of water. It spans four time zones. Brazil is the only country in the world that has the equator and the Tropic of Capricorn running through it. It is also the only country to have contiguous territory both inside and outside the tropics. Brazilian topography is also diverse and includes hills, mountains, plains, highlands, and scrublands. Much of the terrain lies between 200 metres (660 ft) and 800 metres (2,600 ft) in elevation. The main upland area occupies most of the southern half of the country. The northwestern parts of the plateau consist of broad, rolling terrain broken by low, rounded hills. Brazil has a dense and complex system of rivers, one of the world's most extensive, with eight major drainage basins, all of which drain into the Atlantic.[146] Major rivers include the Amazon (the world's second-longest river and the largest in terms of volume of water), the Paraná and its major tributary the Iguaçu (which includes the Iguazu Falls), the Negro, São Francisco, Xingu, Madeira and Tapajós rivers.

Capital City: Brasilia
Largest City: Sau Paulo
National Language: Portuguese
Currency: Real (R$)
October - France
November - Canada
December - South America
January - Norway
February - Cuba
March - Thailand
April - Japan
May - Mexico
June - U.S.A.




































































































































![Territory of the French Republic[I]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/9e/French_republic%2BEEZ_without_Antarctica-en.svg/250px-French_republic%2BEEZ_without_Antarctica-en.svg.png)





















































No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.